11:20am - 11:39am | Efficient Reinforcement Learning
Speakers: Rhythm Garg & Linden Li (both Co-founders, Applied Compute)
Speaker Profiles: Rhythm Garg | Linden Li
Bio: Co-founders, Applied Compute
Topic: RL mechanisms for building superhuman agents and discussing proprietary RL stack for efficient model training




Notes
- how do we push AI past productivity into real stuff
- deploy with a data fly wheel
- RL is the tool that they use
- how does high computer RL help LLM learn to reason
- get a model, and try it 100s of times
- grade the answers
- when it’s correct, reinforce the thinking path for each one
- applied computer is different from the labs
- need the runs to be fast
- cheap
- predictable (generally low variance)
- can we build
- naive sync rl
- no
- async rl — pipeline RL is their preferred one
- inflight weight update
- some tokens are from previous weights, sometimes multiple gens back
- variance increases as you increase staleness
- want staleness for fast runs, but staleness makes training unstable and requires advancements
- assuming we know that, what is the high throughput way to do RL
- surprising far with some first principal modeling problem
- n_gpus is cast member #1
- harder to calculate with async because they can split
- training_batch_size
- sample n problems in parallel
- sampling through
- KV Cache memory
- we should be estimated the base kv cache
- forward pass latency per GPU
- training_throughput_per_gpu
- n_gpus is cast member #1
- really focused on maximizing GPU usage for training run
- async
- too many training but not enough sampling
- no good
- too many samples
- no good either
- too many training but not enough sampling
- delicate balanced and they seemed to know
- surprising far with some first principal modeling problem
Slides
Slide: 2025-11-21-11-22

Key Point: Academic research introducing PipelineRL, a method for improving the efficiency of on-policy reinforcement learning when generating long sequences, positioning it as a contribution to both research and practical implementation.
Literal Content:
- Title: “PipelineRL: Faster On-policy Reinforcement Learning for Long Sequence Generation”
- Authors listed: Alexandre Piché, Elissa Kanooloo, Rafael Pardinas, Xingyu Chen, Dzmitry Bahdanau
- Affiliations: Armanadies AI Research team
- ArXiv reference: arXiv:2309.16128v2 [cs.LG]
- Abstract section with technical details about reinforcement learning for sequence generation
Slide: 2025-11-21-11-24

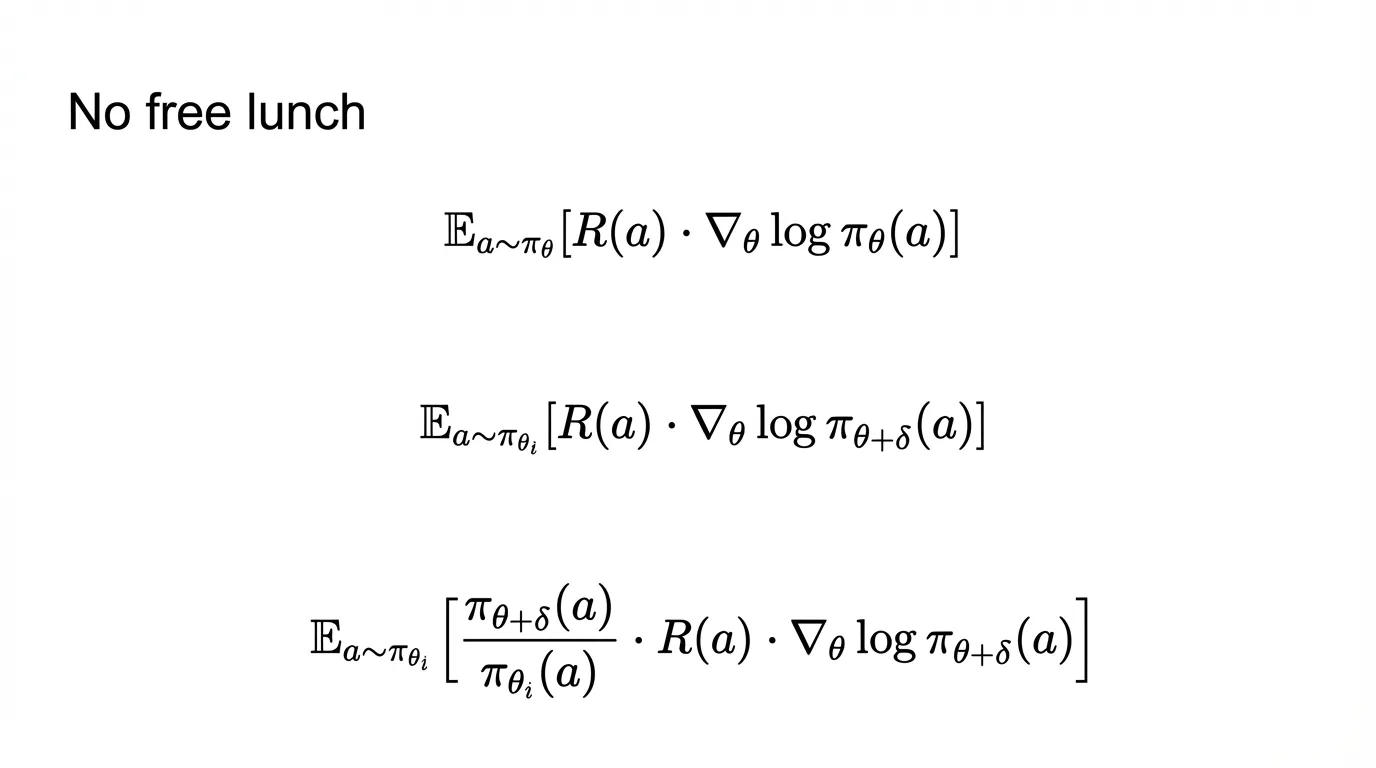
Key Point: Explaining the fundamental tradeoff in reinforcement learning - there’s “no free lunch” when it comes to optimizing policies. The mathematical progression shows how policy gradient methods become more complex when dealing with off-policy learning.
Literal Content:
- Title: “No free lunch”
- Three mathematical formulas showing expectation equations with policy gradients
- Progressive complexity in the formulas, introducing importance sampling weights
Slide: 2025-11-21-11-34

Key Point: Explaining key constraints when optimizing the layout of training and inference infrastructure - balancing token throughput between training and inference, and ensuring staleness doesn’t exceed acceptable limits.
Literal Content:
- Pink background
- Title: “Figuring out the optimal layout”
- Section titled “Invariants:”
- Training token consumption rate == Inference token production rate (with mathematical formula)
- Max theoretical staleness does not exceed what our ML can handle (with formula for max_staleness)
